PCOS can make losing weight feel impossible. You might have tried every diet under the sun, only to find that nothing works. Counting macros and micros could be a game-changer for you. The first step is understanding what they are. In this article, we’ll break down the role of macros in weight loss for PCOS and how to count them effectively. With our new AI tool, counting macros has never been easier. What are macros and micros?
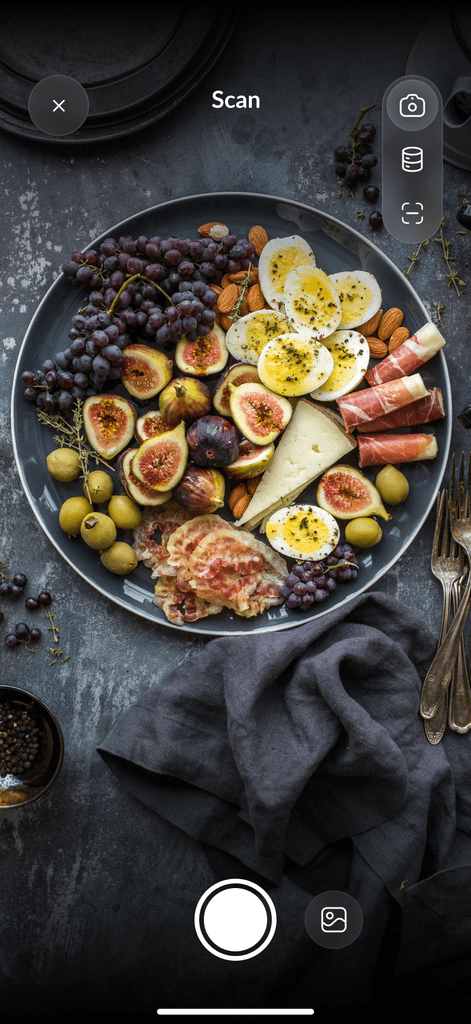
Macros for PCOS weight loss can help you regain control of your health and shed those stubborn pounds. Our AI Calorie Counter will not only help you count macros, but it will also do it for you. With our app, you can scan barcodes and take pictures of food to get instant results. It doesn’t get much easier than that!
Table of Contents
Should You Take Macros for PCOS Weight Loss?

Protein Power: The Key Macronutrient for PCOS
Protein is vital for those with PCOS. It helps you feel full, reducing your overall calorie consumption. A higher protein intake also supports muscle building, essential for a healthy metabolism. Aim for 30% of your daily calories from protein, or about 1.2-1.5g per kg of body weight.
Healthy Fats: Why They Matter
Healthy fats, like those in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, are crucial for hormone production and overall health. Including healthy fats in your diet can promote satiety and help regulate blood sugar levels. Aim for around 30-35% of your daily calorie intake from fats.
Carbohydrates: Not All Are Created Equal
Carbohydrates are your body's primary energy source, but some can spike blood sugar levels and worsen insulin resistance. To help manage blood sugar levels, focus on low-glycemic, fiber-rich carbohydrates, such as whole grains, vegetables, and fruits. Limit refined carbohydrates and sugary foods, and consider a moderate carbohydrate intake, potentially between 40-50% of your daily calories, depending on your individual needs and activity level.
Water: The Unsung Hero of Weight Loss
Hydration is crucial for overall health and can play a role in weight management. Adequate water intake can help with satiety, digestion, and overall metabolic function. Aim for at least 3-3.5 liters of water per day.
Calorie Deficit: The Simple Science of Weight Loss
To lose weight, consuming fewer calories than you burn is essential. By carefully controlling your macronutrient intake and overall calorie consumption, you can create a calorie deficit that leads to weight loss. Work with a healthcare professional or registered dietitian to determine a sustainable and healthy calorie intake for your needs.
Ideal Macros for PCOS Weight Loss

Protein: The Key Player for Your PCOS Diet
Women with PCOS should aim for 30% of their daily calories from protein. This translates to approximately 1.2-1.5 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, or 25-35 grams per meal. Protein helps regulate blood sugar, reduce insulin resistance, and promote satiety, aiding in weight management. Research shows that high-protein diets can help with weight loss and improve metabolic health in women with PCOS.
Carbohydrates: Picking the Right Types for PCOS Weight Loss
Carbohydrates should make up around 40% of your daily calories. Prioritize low-glycemic carbohydrates like whole grains, fruits, and vegetables over processed foods and refined sugars. Fiber-rich carbohydrates help control blood sugar and can contribute to feeling fuller, potentially reducing overall calorie intake.
Fats: Don’t Be Afraid of Them!
Healthy fats should contribute to 30-35% of your daily calories. Focus on sources like nuts, seeds, avocados, fatty fish (salmon, tuna, sardines), and olive oil. Fats are essential for overall health and can contribute to satiety.
Related Reading
• Do Minerals Have Calories
• How Long in a Calorie Deficit to See Results
• How to Use a Food Scale to Lose Weight
• Can You Eat Pizza on a Diet
• Do Carbs Make You Fat
• Why Am I Not Losing Fat in a Calorie Deficit
• What Are Net Calories
• Is the Fitness App Accurate
• How Many Calories Below Bmr to Lose Weight
How to Lose Weight on PCOS in 9 Ways

1. Reduce Your Carb Intake
Cutting back on carbs is a smart strategy for losing weight with PCOS. Decreasing carbohydrate consumption may help manage PCOS due to its impact on insulin levels. Insulin resistance occurs when your cells respond abnormally to the hormone insulin. Between 35% and 80% of people with PCOS experience this. Insulin is necessary for blood sugar regulation and energy storage in the body. Research suggests that high levels of insulin are linked to increased body fat and weight gain in the general population and people with PCOS.
2. Get Plenty of Fiber
As fiber helps you stay full after a meal, a high fiber diet may promote weight loss in people with PCOS. In the United States, the dietary reference intake for fiber is 14 grams (g) per 1,000 calories, or around 25 g per day for women. However, most Americans consume only about 15 g of fiber per day. In a 2019 study, researchers linked higher fiber intake to lower insulin resistance, less total body fat, and less belly fat in people with PCOS.
3. Eat Enough Protein
Protein helps stabilize blood sugar and increases feelings of fullness after a meal. It may also aid weight loss by reducing cravings, helping burn more calories, and regulating hunger hormones. In an older 2012 study, 57 people with PCOS consumed either a high protein diet consisting of more than 40% of calories from protein and 30% from fat or a standard diet comprising less than 15% from protein and 30% from fat.
Individuals in the high protein group lost an average of 9.7 pounds (4.4 kilograms) after 6 months, significantly more than those in the control group. If you’re concerned you’re not getting enough protein, consider adding it to your meals or choosing high-protein snacks. Healthy high-protein foods include eggs, nuts, dairy, meat, and seafood.
4. Eat Healthy Fats
Plenty of healthy fats in your diet may help you feel more satisfied after meals and tackle weight loss and other symptoms of PCOS. Avocado, olive oil, coconut oil, and nut butter are some foods that contain healthy fats. Combining healthy fat with a protein source can further increase the filling effects of meals and snacks.
5. Eat Fermented Foods
Healthy gut bacteria may play a role in metabolism and weight maintenance. Studies suggest that people with PCOS may have fewer healthy gut bacteria than those without this condition. Emerging research suggests that certain probiotic strains positively affect weight loss. However, other research has produced mixed results. Still, eating foods high in probiotics such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and other fermented foods may help increase the amount of beneficial bacteria in your gut.
6. Limit Processed Foods and Added Sugars
Another tip to lose weight with PCOS is to cut down on your intake of less nutritious foods. Processed foods and added sugars may raise blood sugar levels and increase your risk of insulin resistance, which is linked to obesity. People with PCOS may process sugar differently than those without it.
Research shows that women with PCOS experience larger spikes in blood sugar and insulin levels after consuming the same amount of sugar as women without this condition. Experts recommend that people with PCOS limit their consumption of added sugars and refined carbs. This may help them manage symptoms and maintain a moderate body weight. Foods with added sugar and refined carbs include cakes, cookies, candy, and fast food.
7. Exercise Regularly
Exercise is a well-known strategy for increasing weight loss. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends 30 minutes of moderate activity 5 days per week for a total of 150 minutes of moderate activity per week. While people with PCOS lost less fat than those without this condition, the exercise regimen did result in a loss of belly fat and improved insulin sensitivity.
8. Get Enough Sleep
Experts increasingly acknowledge sleep as central to overall health. If you have PCOS, you may experience sleep disturbances, including excessive daytime sleepiness, sleep apnea, and insomnia. Lack of sleep has been shown to increase the activity of hormones that drive hunger, such as ghrelin and cortisol, which may cause you to eat more throughout the day. Researchers have linked insufficient sleep with a higher risk of being overweight or obese. The CDC suggests that adults should aim for at least 7 hours of sleep each night.
9. Manage Your Stress
Stress can be a risk factor for weight gain. This means reducing stress levels may help you manage your weight. Stress increases levels of cortisol, a hormone that your adrenal glands produce. Chronically high cortisol levels are linked to insulin resistance and weight gain. Chronic stress also increases your risk of gaining belly fat. In turn, belly fat increases inflammation, which triggers your body to make more cortisol, creating a vicious cycle. To lower your cortisol levels, consider incorporating stress management techniques into your day-to-day life, such as practicing yoga, spending time in nature, practicing meditation, and spending more time doing things you enjoy.
How to Count Calories on PCOS

Leverage Technology to Track Your Macros: Diet AI to the Rescue
DietAI transforms calorie counting with our AI calorie-counting app. Take a picture of your food, and our app instantly analyzes your meals from a simple photo, delivering accurate calorie and macro information without manual logging. Beyond photo recognition, the app provides comprehensive progress tracking, personalized nutrition insights tailored to your goals, and convenient barcode scanning for packaged foods.
Whether trying to lose weight, gain muscle, or simply maintain a balanced diet, DietAI makes nutrition tracking effortless by eliminating the tedious aspects of traditional food journaling. Download now to effortlessly track your calories and macros with DietAI, the AI-powered app that makes logging meals as simple as snapping a photo. Download today for 80% off!
Figure Out Your Caloric Needs
Caloric requirements vary based on age, weight, activity level, and metabolic rate. For illustrative purposes, Plano uses a 1,400-calorie daily intake as a starting point for weight loss in women with PCOS. However, it's advisable to consult with a registered dietitian to determine your personalized caloric needs.
Determine Your Macro Ratios
Once you know how many calories you should eat, it’s time to allocate your macros. Plano recommends the following macronutrient distribution for women with PCOS:
Carbohydrates
Less than 40% of total calories
Protein
Approximately 30% of total calories Fat: Approximately 30% of total calories.
Calculate Your Macros
Using the 1,400-calorie example:
Carbohydrates: 40% of 1,400 = 560 calories → 560 ÷ 4 (calories per gram) = 140 grams
Protein: 30% of 1,400 = 420 calories → 420 ÷ 4 = 105 grams
Fat: 30% of 1,400 = 420 calories → 420 ÷ 9 (calories per gram) ≈ 47 grams
Choose Nutrient-Dense Foods
Carbohydrates: Focus on complex carbohydrates like whole grains, legumes, and starchy vegetables, which digest slowly and help regulate blood sugar levels.
Protein
Incorporate lean proteins such as poultry, fish, eggs, and plant-based sources like legumes and tofu to promote satiety and support metabolic functions.
Fats
Opt for healthy fats from sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, which support hormone production and overall health.
Related Reading
• Carnivore Macros for Weight Loss
• How to Track Calories When Eating Out
• Weight Watchers vs Calorie Counting
• Macros for Mediterranean Diet
• How to Stick to a Calorie Deficit
• Losing Weight and Gaining Muscle
• How to Track Alcohol Macros
• Macros for 1200 Calorie Diet
• Intermittent Fasting and Macros
• Paleo Macros
Download DietAI Today for 80% Off!
Macronutrients, or macros, are the nutrients that provide us with energy, measured in calories. There are three primary macronutrients: carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. Each macro plays a unique role in bodily function. For example, carbohydrates are the body’s main source of energy, while proteins help build and repair tissues, and fats support cell structure and hormone production. Each macro affects the body differently, and the right balance can vary based on individual goals, preferences, lifestyle, and health conditions like PCOS.
Why Track Macros?
Tracking macros can help take the guesswork out of dieting. While traditional calorie counting focuses on reducing overall energy intake, tracking macros allows for more personalized nutrition. Changing your body composition can also impact health. For example, losing weight can help reduce insulin resistance and restore ovulatory function in people with PCOS.
Whether trying to lose weight, gain muscle, or simply maintain a balanced diet, DietAI makes nutrition tracking effortless by eliminating the tedious aspects of traditional food journaling. Download now to effortlessly track your calories and macros with DietAI, the AI-powered app that makes logging meals as simple as snapping a photo. Download today for 80% off!
Related Reading
• Vegan Macros
• Endomorph Macros for Fat Loss
• Hitting Macros but Not Calories
• Ketosis vs Calorie Deficit
• Macros for Menopause Weight Loss
• Macros for Bariatric Patients
• Nutracheck vs Myfitnesspal
• Noom vs Myfitnesspal
• MacroFactor vs Carbon