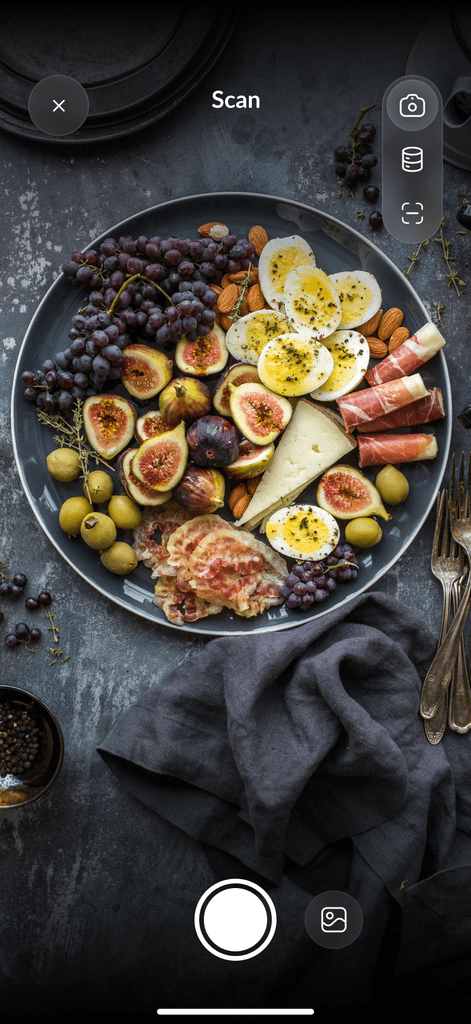
Macro counting isn't just about eating fewer carbs or fats. It’s about eating the right foods to shed fat while preserving muscle. For this reason, counting macros can take time and dedication. If you want to lose weight and maintain muscle, it pays to track the right macronutrients geared toward your cutting goals. So, how to track macros?
This guide will help you learn how to split macros for cutting. We'll also show you how to count calories faster with AI to make your cutting journey more manageable. You can get started today with Diet AI's calorie counter. This tool can help you reach your goals and stay on track so you can stop stressing about dieting.
Table of Content
Benefits of Using Macros for Cutting

Understanding Macronutrients Will Help You Lose Weight
If you want to lose weight, counting or tracking your macronutrients for a short time will help you understand where your calories are coming from. “A lot of people don’t know the macronutrient content of their food,” Albert says. “If you’re eating 2,000-2,500 calories per day, but most of these calories are coming from simple carbs, then you’re more likely to gain weight.”
Simple carbohydrates, found in foods like baked goods and white bread, are digested quickly, giving you a sugar rush but leaving you feeling fatigued. Complex carbohydrates, such as whole grains and fiber-rich vegetables, are digested more slowly.
Each macronutrient plays a role in keeping your body full and satisfied, which helps to prevent overeating, reduces cravings, and enables you to lose weight. “Calories are important for weight loss, but understanding macronutrients will help you stay on track and achieve long-term weight loss,” Albert says.
Related Reading
• Apple Diet
• Macros for Muscle Gain
• Best Macro Tracking App
• Best App to Track Macros
• Macro Diet Plan
• Macro Ratio for Weight Loss
What are the Best Macros for Cutting?

Protein: The Body's Builder
Proteins contain amino acids. Each gram of protein provides 4 kilocalories, but your body does not use protein as a primary energy source. Protein is primarily a nutrient that builds muscle, prevents muscle loss, supports the immune system, and produces hormones, enzymes, and neurotransmitters.
Sufficient protein intake is critical for losing fat while maintaining muscle mass. Losing muscle mass can decrease resting energy expenditure over the long term, making losing and maintaining weight harder.
Although optimal protein intake will vary by person, guidelines recommend at least 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight. A person who weighs 70 kilograms needs 56 grams of protein to meet the minimal protein requirement. Inadequate protein intake can cause muscle loss, decreased bone mass, impaired hormone production, anemia, and skin issues.
Carbohydrates: The Energy Source
Carbohydrates are the body's primary energy source. They provide 4 kilocalories per gram. Fiber, a carbohydrate found mainly in complex carbohydrates, is essential for gut and immune function and helps maintain metabolic and heart health. If you don't get enough carbohydrates, your body will still produce energy from fats and protein.
Your body's use of protein for energy can cause you to lose muscle mass. Restricting carbohydrate intake can tax your body, and many people find it difficult to maintain energy and motivation. It also limits the intake of essential nutrients. On the other hand, excess carbohydrate intake can cause you to exceed your calorie intake.
People with prediabetes and diabetes can develop serious health problems when they eat too few carbohydrates. Due to decreased carbohydrate intake, limited fiber intake can also contribute to higher cholesterol and blood glucose levels and negatively impact your gut health.
Fats: The Energy-Dense Nutrient
Fats provide the most energy: 9 kilocalories per gram. They regulate body temperature, produce sex hormones, contribute to cell structures, and help absorb fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K). While your body needs fat, a diet consisting primarily of unsaturated fats over saturated fats is recommended.
Unsaturated fats include olive oil, nuts, seeds, fatty fish, and avocados. Saturated fats naturally exist in animal-based foods and are higher in fast and processed foods. While unsaturated fats are associated with health benefits, saturated fats can increase cholesterol levels and the risk of heart disease.
Ideal Macro Split for Cutting

Cutting Macros 101: The Breakdown of Macronutrients for Fat Loss
When you're on the cutting diet, your body will need fewer calories to maintain its new weight. But just because you are eating less doesn't mean you should stop eating your favorite foods or that all foods are created equal. The number of calories you consume is essential for fat loss, but so is the quality. To ensure your body has enough nutrients to function correctly while losing fat and to help preserve muscle mass, it's crucial to track macros on a cutting diet.
Setting Macro Targets for Cutting
A high protein, moderate fat, and mild to low carbohydrate macro split, such as 40% protein, 30% carbs, and 30% fat, is generally recommended for cutting and fat loss. In contrast, a 50:30:20 split (protein, carbs, fat) can also be effective. Here's a more detailed breakdown:
Protein
Aim for 40% of your daily calories from protein to help preserve muscle mass during a calorie deficit.
Carbohydrates
Moderate to low carbohydrate intake (30% of calories) can help with fat loss while still providing energy for workouts.
Fats
Moderate fat intake (30% calories) is essential for hormone production, nutrient absorption, and overall health.
Alternative Split
A 50:30:20 split (protein, carbs, fat) can also be effective, especially for more active people who need more carbohydrates for energy.
Individualization
These are just guidelines, and your ideal macro split may vary based on your individual needs, activity level, and goals.
Focus on Quality
Regardless of your macro split, prioritize whole, unprocessed foods for optimal health and results.
Download DietAI Today for 80% Off!

DietAI transforms calorie counting with our AI calorie counting app. Take a picture of your food, and our app instantly analyzes your meals from a simple photo, delivering accurate calorie and macro information without manual logging. Beyond photo recognition, the app provides comprehensive progress tracking, personalized nutrition insights tailored to your goals, and convenient barcode scanning for packaged foods.
Whether you are trying to lose weight, gain muscle, or simply maintain a balanced diet, DietAI makes nutrition tracking effortless by eliminating the tedious aspects of traditional food journaling. Download now to effortlessly track your calories and macros with DietAI, the AI-powered app that makes logging meals as simple as snapping a photo. Download today for 80% off!
Related Reading
• Low Carb Macros
• Macro Foods
• Macro Ratio for Muscle Gain
• Best Macros for Fat Loss
• 40 30 30 Diet
• Macro Ratios
How to Count Macros for Cutting in 5 Simple Steps

1. Use Diet AI: The Macro Counter That Makes Cutting Easy
Counting macros while cutting doesn't have to be tedious. In fact, with the right tools, it can be quick and even fun. DietAI is an app that transforms calorie counting with AI. Simply take a picture of your food, and our app instantly analyzes your meals from a simple photo, delivering accurate calorie and macro information without manual logging.
Beyond photo recognition, the app provides comprehensive progress tracking, personalized nutrition insights tailored to your goals, and convenient barcode scanning for packaged foods.
Whether you are trying to lose weight, gain muscle, or simply maintain a balanced diet, DietAI makes nutrition tracking effortless by eliminating the tedious aspects of traditional food journaling. Download now to effortlessly track your calories and macros with DietAI, the AI-powered app that makes logging meals as simple as snapping a photo.
2. Estimating Protein Needs: The Most Important Macro For Cutting
Research supports higher protein intake during a calorie deficit for many reasons, mainly improved body composition. High-protein diets help protect lean muscle mass while cutting calories and, in some cases, can help you gain a small amount of muscle while losing fat. Reduced hunger and cravings are another reason to prioritize protein while cutting. Protein is incredibly satiating and may also play a role in reducing sugar cravings.
Protein is the single most important macro to consider when cutting. You will likely get incredible results if you only focus on hitting your daily calories and getting enough protein. Your protein needs are based on how many pounds of lean mass you have, so if you know your current body composition, you can easily calculate exactly how many grams of protein you need daily.
Aim to get at least 1 gram of protein per pound of lean body mass for maintenance. Or, based on existing research, you should aim to get roughly 0.8 to 1.2 grams of protein per pound of body weight. For example, A 200-pound adult should get 160 to 240 grams of protein daily while cutting.
3. Start High, Go Slow: How to Start a High-Protein Diet for Cutting
Like decreasing calorie intake, jumping into a very high-protein diet can be difficult if you’re not already eating enough protein. You can use a similar approach to increasing protein intake as you do cutting calories by gradually increasing this macro over time.
Start at a moderate amount, around 0.8 to 0.85 grams of protein per pound of body weight, and increase with each phase of your diet. For example, A 200-pound adult can structure their protein macros like so: Weeks 1-4 at 160 grams/day (0.80 grams/pound of body weight) Weeks 5-8 at 180 grams/day (0.90 grams/pound of body weight) Weeks 9-12 at 200 grams/day (1.0 grams/pound of body weight)
4. Figure Out Your Daily Fat Needs
Often, a diet cuts fat to very low levels, but this isn’t always necessary. Eating fat won't make you fat, significantly when you are decreasing calories in the first place. Dietary fat is essential for health and can make your diet feel a bit more satisfying by adding flavor to food.
Moreover, fat is a source of long-lasting energy; some find a higher fat intake more enjoyable. To ensure you aren't cutting fat too low, aim to get anywhere from 20% to 40% of your calories from fat. Because carbs will fill the gap in your remaining calorie needs, you can calculate dietary fat amounts based on your activity level.
The more active you are, the more carbs you need to scale fat to the lower end of the spectrum. Whereas those who need fewer carbs can increase their fat to the higher end. For example: If you are eating 2,000 calories a day your daily fat needs would look like the following: 89 grams of fat/day if you are lightly active (2,000 x 40%) 67 grams of fat/day for moderately active (2,000 x 30%) 45 grams of fat/day if you are very active (2,000 x 20%)
5. Determine Your Daily Carb Needs
The remainder of your calories will come from carbohydrates. Your carbohydrate needs directly depend on how much exercise you get and the type of exercise. As a rule of thumb, the more active you are, the more carbs your body can utilize and store efficiently. Additionally, the more muscle mass you have, the better your body can tolerate a higher carb intake.
This is because most sugar is stored in your lean tissue as a reserve fuel for exercise and daily movement. By estimating fat needs based on activity level, you can assume your remaining calories are sufficient to meet your basic carbohydrate needs. You can easily calculate your carb needs by subtracting your fat and protein calories from your daily calories.
For example: If you need 2,000 calories a day, 160 grams of protein, and 67 grams of fat, your carb needs would look like so: 2,000 calories - 640 protein calories (160 grams x 4 calories/gram) - 603 fat calories (67 grams x 9 calories/gram) = 757 calories from carbs 757 calories/4 calories per gram = 190 grams of carbs a day Aim to choose high-quality carbohydrates from whole foods like sweet potatoes, quinoa, and whole-wheat pasta as these also contain other beneficial vitamins and minerals along with reasonable amounts of dietary fiber to support your gut health.
Download DietAI Today for 80% Off!
DietAI transforms calorie counting with our AI calorie counting app. Take a picture of your food, and our app instantly analyzes your meals from a simple photo, delivering accurate calorie and macro information without manual logging. Beyond photo recognition, the app provides comprehensive progress tracking, personalized nutrition insights tailored to your goals, and convenient barcode scanning for packaged foods.
Whether you are trying to lose weight, gain muscle, or simply maintain a balanced diet, DietAI makes nutrition tracking effortless by eliminating the tedious aspects of traditional food journaling. Download now to effortlessly track your calories and macros with DietAI, the AI-powered app that makes logging meals as simple as snapping a photo. Download today for 80% off!
Related Reading
• MyFitnessPal Alternatives
• Macros for Dummies
• Macro Diet for Beginners
• Lean Bulk Diet Plan
• How to Track My Macros
• Top Calorie Counting Apps