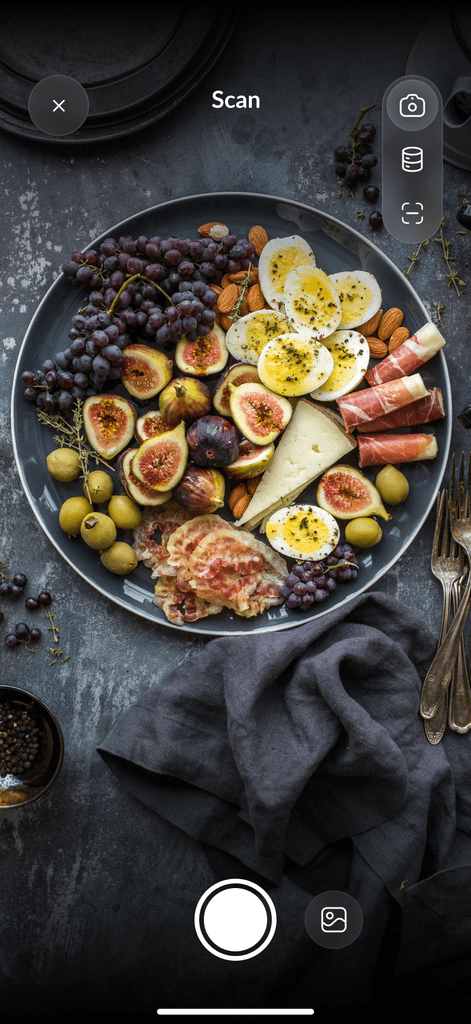
What if you could lose weight while eating your favorite foods? For many, the idea is too good to be true. However, once you understand what are macros and micros, it makes sense. You first need to create a calorie deficit regarding weight loss. From there, counting macros and micros can help you lose weight faster and get better results.
Calorie deficits, macros, and micros can get complicated, though. Many people find it challenging to navigate the complexities of dieting and give up before they see any results. This guide will address one of your first challenges when starting a new diet: How many calories below BMR to lose weight? By understanding how many calories below your BMR you should eat to lose weight, you can more easily create the proper diet to help you reach your goals. We’ll also explain how tools like DietAI's calorie counter can help you get there faster.
Table of Contents
What is BMR?

Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is often used interchangeably with resting metabolic rate (RMR). While BMR is the minimum number of calories required for essential functions at rest, RMR — also called resting energy expenditure (REE) — is the number of calories your body burns. Although BMR and RMR slightly differ, your RMR should accurately estimate your BMR. The two values tend to vary by about 10%.
How to Estimate Your BMR
One popular way to estimate Trusted Source BMR is through the Harris-Benedict formula, which considers weight, height, age, and sex.
Females assigned at birth (FAABs) BMR = 655 + (9.6 x weight in kg) + (1.8 x height in cm) – (4.7 x age in years)
Males assigned at birth (MAABs) 66 + (13.7 x weight in kg) + (5 x height in cm) – (6.8 x age in years)
How Many Calories Below BMR to Lose Weight

Caloric Deficit For Weight Loss: How Many Calories Do You Need Below BMR To Lose Weight?
You must consume fewer calories than your TDEE to lose weight, creating a caloric deficit. A common and sustainable approach is to reduce your daily intake by approximately 500 calories below your TDEE. This deficit can result in a weight loss of about one pound per week, as approximately 3,500 calories equate to one pound of body weight.
Why You Should Never Eat Below Your BMR
Do Not Eat Below Your BMR
Consuming fewer calories than your BMR can deprive your body of the essential energy needed for vital functions, potentially leading to health complications. Always ensure your caloric intake meets or exceeds your BMR.
Adjust Your Deficit Based On Activity Level
Adjust Based on Activity Level
Your TDEE accounts for physical activity. If you increase your activity level, your TDEE will increase, allowing for a higher caloric intake while maintaining a deficit.
Monitor Your Progress And Adjust As Needed
Monitor and Adjust
Track your progress regularly and adjust your caloric intake and activity levels to continue achieving your weight loss goals.
Related Reading
• Do Minerals Have Calories
• How Long in a Calorie Deficit to See Results
• How to Use a Food Scale to Lose Weight
• Can You Eat Pizza on a Diet
• Do Carbs Make You Fat
• Why Am I Not Losing Fat in a Calorie Deficit
• What Are Net Calories
• Is the Fitness App Accurate
How to Burn More Calories

Feeling Stuck? Here’s How to Burn Calories Below BMR
You can burn calories below BMR by limiting your food intake and increasing physical activity. To burn more calories, the Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans recommend the following:
Get Moving With Aerobic Activity
The Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans recommend aerobic activity to burn more calories. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity daily as a general goal. You may need to exercise more to lose weight, maintain weight loss, or meet specific fitness goals. Mild aerobic exercise includes activities such as brisk walking, biking, swimming, and mowing the lawn. Vigorous aerobic exercise includes running, heavy yard work, and aerobic dancing.
Add Strength Training to Your Routine
Another way to increase calorie burn is to add strength training to your routine. The Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans recommend doing strength training exercises for all major muscle groups at least two times a week. Strength training can include using weight machines, your body weight, heavy bags, resistance tubing, resistance paddles in the water, or activities such as rock climbing.
Related Reading
• Carnivore Macros for Weight Loss
• How to Track Calories When Eating Out
• Weight Watchers vs Calorie Counting
• Macros for Mediterranean Diet
• How to Stick to a Calorie Deficit
• Losing Weight and Gaining Muscle
• How to Track Alcohol Macros
• Macros for 1200 Calorie Diet
• Intermittent Fasting and Macros
• Macros for Pcos Weight Loss
• Paleo Macros
How to Count Calories

1. Use DietAI: The Future of Counting Calories
DietAI transforms calorie counting with our AI calorie counting app. Take a picture of your food, and our app instantly analyzes your meals from a simple photo, delivering accurate calorie and macro information without manual logging. Beyond photo recognition, the app provides comprehensive progress tracking, personalized nutrition insights tailored to your goals, and convenient barcode scanning for packaged foods. Whether you are trying to lose weight, gain muscle, or simply maintain a balanced diet, DietAI makes nutrition tracking effortless by eliminating the tedious aspects of traditional food journaling. Download now to effortlessly track your calories and macros with DietAI, the AI-powered app that makes logging meals as simple as snapping a photo. Download today for 80% off!
2. Estimate Your Total Calorie Requirements
Four main formulas estimate calorie requirements. My top choice is the Mifflin-St. Jeor Formula. A systematic review by Frankenfield et al. compared all four equations and found the Mifflin-St. Jeor is to be the most accurate. I have used this formula on myself and various clients throughout my 10 years as a personal trainer, and so far, it hasn’t let me down.
The Formula
Male: (10 x weight kg) + (6.25 x height cm) – (5 x age) + 5
Female: (10 x weight kg) + (6.25 x height cm) – (5 x age) – 161
Example
Alex is a 30-year-old, 80 kg male, 180 cm tall: (10×80) + (6.25 x 180) – (5×30) + 5 = 1,780
3. Multiply the Above Figure by Your Activity Level
The above number is calculated for zero for someone who does not exercise at all. Now you need to factor in the calories burned from exercise. Someone more active will need more calories each day, and vice versa for someone less active. Multiply your total calorie requirements (Step 1 total) by one of the points below that best aligns with your everyday activity level.
Activity Levels
Sedentary (little or no exercise, desk job) x 1.2
Lightly active (light exercise/sports 1-3 days/week) x 1.3-1.4
Moderately active (moderate exercise/sports 3-5 days/week) x 1.5-1.6
Very active (hard exercise/sports 6-7 days per week) x 1.7-1.8
Extremely active (very hard daily exercise/sports & physical job or twice-a-day training) x 1.9-2.0
Example
Alex trains four times per week (moderately active). To calculate his daily calories, we multiply his required calorie count, 1,780, by 1.5-1.6. For this example, we will choose 1.6 because Alex sometimes trains a little more than four times per week: 1,780 x 1.6 = 2,848 calories (this would be our approximate maintenance calories).
4. Setting Macronutrient Targets to Meet These Calories
If you stick to the same activity level, you know how many calories you need daily. The next step is to set mini targets (protein, carbohydrates, and fat) in your total calorie target.
Protein Targets
Protein-rich food:
Standard requirement: 2-3 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight
Muscle growth requirement: 2-2.5 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight
Fat loss requirement: 2.5-3 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight
There are 4 calories per 1 gram of protein. So when calculating your calorie intake, you’ll need to multiply your total grams of protein by 4.
Example 1
Alex wants to lose fat and grow muscle, so the equation we would use for him is: 2.5 x 80 (body weight) = 200 grams of protein (x4 = 800 calories) If you are on a journey to a specific weight, make sure you calculate your protein based on your goal weight, not your current weight. (You can also see my article "Creating a diet plan for weight loss" here.)
Fat Targets
There are 9 calories per 1g of fat, so when calculating your calorie intake, you’ll need to multiply your total grams of fat by 9. The standard requirement is 0.7- 1.1g of fat per kilogram of body weight.
Example
Based on the foods Alex enjoys eating (e.g., avocados, nuts, trimmed bacon), he is closer to a higher-fat diet. This is why we’ll choose the higher amount (1g) to calculate his calories: 1 x 80 = 80g of fat (720 calories).
Carbohydrate Targets
Fill in the remaining calories with carbohydrates. There are 4 calories per 1 gram of carbohydrates. So when calculating your calorie intake, you must multiply your total grams of carbohydrates by 4.
Example
Alex has a total of 2,848 calories. He’s used up 800 on protein and 720 on fat, so he has 1,328 calories left. Divide the remaining calories by 4 to determine how many carbohydrates you can include in your diet: 1,328 divided by 4 = 332 grams.
Download DietAI Today for 80% Off!
Macros is just a short way of saying macronutrients. Macros include carbohydrates, fats, and proteins—nutrients the body needs in large amounts to function properly. Each macro plays a distinct role in bodily function. Carbohydrates are the body’s primary energy source, while protein is primarily responsible for growth, repair, and maintenance of bodily tissues. Fats support several body systems, including the endocrine system, and facilitate the absorption of specific vitamins. Though each has unique functions, macros often work together to support overall health. For example, carbohydrates and fats supply energy, while protein and fat help repair tissues after exercise and support recovery.
DietAI transforms calorie counting with our AI calorie counting app. Take a picture of your food, and our app instantly analyzes your meals from a simple photo, delivering accurate calorie and macro information without manual logging. Beyond photo recognition, the app provides comprehensive progress tracking, personalized nutrition insights tailored to your goals, and convenient barcode scanning for packaged foods.
Whether you are trying to lose weight, gain muscle, or simply maintain a balanced diet, DietAI makes nutrition tracking effortless by eliminating the tedious aspects of traditional food journaling. Download now to effortlessly track your calories and macros with DietAI, the AI-powered app that makes logging meals as simple as snapping a photo. Download today for 80% off!
Related Reading
• Vegan Macros
• Endomorph Macros for Fat Loss
• Hitting Macros but Not Calories
• Ketosis vs Calorie Deficit
• Macros for Menopause Weight Loss
• Macros for Bariatric Patients
• Nutracheck vs Myfitnesspal
• Noom vs Myfitnesspal
• MacroFactor vs Carbon